Benchmarks¶
There are several sets of benchmark designs which can be used with VTR.
VTR Benchmarks¶
The VTR benchmarks [LAK+14, RLY+12] are a set of medium-sized benchmarks included with VTR. They are fully compatible with the full VTR flow. They are suitable for FPGA architecture research and medium-scale CAD research.
Benchmark |
Domain |
|---|---|
bgm |
Finance |
blob_merge |
Image Processing |
boundtop |
Ray Tracing |
ch_intrinsics |
Memory Init |
diffeq1 |
Math |
diffeq2 |
Math |
LU8PEEng |
Math |
LU32PEEng |
Math |
mcml |
Medical Physics |
mkDelayWorker32B |
Packet Processing |
mkPktMerge |
Packet Processing |
mkSMAdapter4B |
Packet Processing |
or1200 |
Soft Processor |
raygentop |
Ray Tracing |
sha |
Cryptography |
stereovision0 |
Computer Vision |
stereovision1 |
Computer Vision |
stereovision2 |
Computer Vision |
stereovision3 |
Computer Vision |
The VTR benchmarks are provided as Verilog under:
$VTR_ROOT/vtr_flow/benchmarks/verilog
This provides full flexibility to modify and change how the designs are implemented (including the creation of new netlist primitives).
The VTR benchmarks are also included as pre-synthesized BLIF files under:
$VTR_ROOT/vtr_flow/benchmarks/vtr_benchmarks_blif
Titan Benchmarks¶
The Titan benchmarks are a set of large modern FPGA benchmarks compatible with Intel Stratix IV [MWL+13, MWL+15] and Stratix 10 [KTK23] devices. The pre-synthesized versions of these benchmarks are compatible with recent versions of VPR.
The Titan benchmarks are suitable for large-scale FPGA CAD research, and FPGA architecture research which does not require synthesizing new netlist primitives.
Note
The Titan benchmarks are not included with the VTR release (due to their size). However they can be downloaded and extracted by running make get_titan_benchmarks from the root of the VTR tree. They can also be downloaded manually.
See also
Koios 2.0 Benchmarks¶
The Koios benchmarks [ABR+21] are a set of Deep Learning (DL) benchmarks. They are suitable for DL related architecture and CAD research. There are 40 designs that include several medium-sized benchmarks and some large benchmarks. The designs target different network types (CNNs, RNNs, MLPs, RL) and layer types (fully-connected, convolution, activation, softmax, reduction, eltwise). Some of the designs are generated from HLS tools as well. These designs use many precisions including binary, different fixed point types int8/16/32, brain floating point (bfloat16), and IEEE half-precision floating point (fp16).
Benchmark |
Description |
|---|---|
dla_like |
Intel-DLA-like accelerator |
clstm_like |
CLSTM-like accelerator |
deepfreeze |
ARM FixyNN design |
tdarknet_like |
Accelerator for Tiny Darknet |
bwave_like |
Microsoft-Brainwave-like design |
lstm |
LSTM engine |
bnn |
4-layer binary neural network |
lenet |
Accelerator for LeNet-5 |
dnnweaver |
DNNWeaver accelerator |
tpu_like |
Google-TPU-v1-like accelerator |
gemm_layer |
20x20 matrix multiplication engine |
attention_layer |
Transformer self-attention layer |
conv_layer |
GEMM based convolution |
robot_rl |
Robot+maze application |
reduction_layer |
Add/max/min reduction tree |
spmv |
Sparse matrix vector multiplication |
eltwise_layer |
Matrix elementwise add/sub/mult |
softmax |
Softmax classification layer |
conv_layer_hls |
Sliding window convolution |
proxy |
Proxy/synthetic benchmarks |
The Koios benchmarks are provided as Verilog (enabling full flexibility to modify and change how the designs are implemented) under:
$VTR_ROOT/vtr_flow/benchmarks/verilog/koios
To use these benchmarks, please see the documentation in the README file at: https://github.com/verilog-to-routing/vtr-verilog-to-routing/tree/master/vtr_flow/benchmarks/verilog/koios
MCNC20 Benchmarks¶
The MCNC benchmarks [Yan91] are a set of small and old (circa 1991) benchmarks. They consist primarily of logic (i.e. LUTs) with few registers and no hard blocks.
Warning
The MCNC20 benchmarks are not recommended for modern FPGA CAD and architecture research. Their small size and design style (e.g. few registers, no hard blocks) make them unrepresentative of modern FPGA usage. This can lead to misleading CAD and/or architecture conclusions.
The MCNC20 benchmarks included with VTR are available as .blif files under:
$VTR_ROOT/vtr_flow/benchmarks/blif/
The versions used in the VPR 4.3 release, which were mapped to 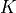 -input look-up tables using FlowMap [CD94], are available under:
-input look-up tables using FlowMap [CD94], are available under:
$VTR_ROOT/vtr_flow/benchmarks/blif/<#>
where 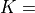
<#>.
Benchmark |
Approximate Number of Netlist Primitives |
|---|---|
alu4 |
934 |
apex2 |
1116 |
apex4 |
916 |
bigkey |
1561 |
clma |
3754 |
des |
1199 |
diffeq |
1410 |
dsip |
1559 |
elliptic |
3535 |
ex1010 |
2669 |
ex5p |
824 |
frisc |
3291 |
misex3 |
842 |
pdc |
2879 |
s298 |
732 |
s38417 |
4888 |
s38584.1 |
4726 |
seq |
1041 |
spla |
2278 |
tseng |
1583 |
SymbiFlow Benchmarks¶
SymbiFlow benchmarks are a set of small and medium sized tests to verify and test the SymbiFlow-generated architectures, including primarily the Xilinx Artix-7 device families.
The tests are generated by nightly builds from the symbiflow-arch-defs repository, and uploaded to a Google Cloud Platform from where they are fetched and executed in the VTR benchmarking suite.
The circuits are the following:
Benchmark |
Description |
|---|---|
picosoc @100 MHz |
simple SoC with a picorv32 CPU running @100MHz |
picosoc @50MHz |
simple SoC with a picorv32 CPU running @50MHz |
base-litex |
LiteX-based SoC with a VexRiscv CPU booting into a BIOS only |
ddr-litex |
LiteX-based SoC with a VexRiscv CPU and a DDR controller |
ddr-eth-litex |
LiteX=based SoC with a VexRiscv CPU, a DDR controller and an Ethernet core |
linux-litex |
LiteX-based SoC with a VexRiscv CPU capable of booting linux |
The SymbiFlow benchmarks can be downloaded and extracted by running the following:
cd $VTR_ROOT
make get_symbiflow_benchmarks
Once downloaded and extracted, benchmarks are provided as post-synthesized blif files under:
$VTR_ROOT/vtr_flow/benchmarks/symbiflow
NoC Benchmarks¶
NoC benchmarks are composed of synthetic and MLP benchmarks and target NoC-enhanced FPGA architectures. Synthetic benchmarks include a wide variety of traffic flow patters and are divided into two groups: 1) simple and 2) complex benchmarks. As their names imply, simple benchmarks use very simple and small logic modules connected to NoC routers, while complex benchmarks implement more complicated functionalities like encryption. These benchmarks do not come from real application domains. On the other hand, MLP benchmarks include modules that perform matrix-vector multiplication and move data. Pre-synthesized netlists for the synthetic benchmarks are added to VTR project, but MLP netlists should be downloaded separately.
Note
The NoC MLP benchmarks are not included with the VTR release (due to their size). However they can be downloaded and extracted by running make get_noc_mlp_benchmarks from the root of the VTR tree. They can also be downloaded manually.